Executive Summary:
This analysis examines how pharmaceutical companies are transforming regulatory compliance from a cost center into a strategic advantage.
| Category | Key Findings |
| Investment & Risk | • $50B annual global compliance spending • $12M+ cost per significant compliance failure • $1.1B in industry penalties over past five years |
| Core Challenges | • Rapidly evolving multi-jurisdictional regulations • Data integrity across 50-200 computerized systems • Global supply chain complexity • 40% of quality professionals retiring by 2030 |
| Strategic Solutions | • Technology-enabled compliance systems • Predictive analytics for risk identification • Quality-focused organizational culture • Continuous process verification |
| Business Impact | • 98-99% batch right-first-time rates for leaders • 22% reduction in quality-related costs • 15% improvement in gross margins • 16% higher market share growth |
This article provides pharmaceutical executives with actionable frameworks to navigate regulatory complexity while enhancing operational performance and competitive positioning.
Introduction:
The pharmaceutical industry faces unprecedented scrutiny. In 2023, manufacturers globally poured $50 billion into pharma regulatory compliance; a figure that continues to climb by 7.17% annually [1]. Despite these massive investments, compliance failures resulted in $1.1 billion in penalties over the past five years [2].

The numbers tell a sobering story: a single significant compliance misstep now triggers remediation costs exceeding $12 million [3], not counting the incalculable damage to patient trust and company reputation.
This article dives into the evolving landscape of pharma regulatory compliance, exploring how forward-thinking companies transform this traditional cost center into a competitive advantage.
1. The Multi-Headed Hydra of Global Regulations
Pharmaceutical manufacturers navigate perhaps the most complex regulatory environment on the planet. A typical facility must simultaneously satisfy requirements from:
| Regulatory Body | Jurisdiction | Key Focus Areas |
| FDA | United States | GMP compliance, inspections, data integrity |
| EMA | European Union | Marketing authorizations, pharmacovigilance |
| PMDA | Japan | Safety standards, post-market surveillance |
| NMPA | China | Product registrations, manufacturing oversight |
| WHO | Global | International standards, prequalification |
“Imagine playing five different chess games simultaneously, where the rules keep changing mid-match,” explains M.R., a compliance professional with 20 years in the industry. “That’s what pharma regulatory compliance feels like today.”
The regulatory landscape grows more demanding by the year. FDA warning letters jumped 42% between 2020-2023, with data integrity violations driving nearly half of all citations [4]. Meanwhile, the EMA’s revised Annex 1 for sterile products forced manufacturers to completely rethink contamination control strategies [5], often requiring multi-million dollar facility upgrades.
This complexity compounds when factoring in global supply chains. With 73% of active pharmaceutical ingredients for U.S. drugs manufactured overseas, quality assurance teams must bridge vast distances, cultural differences, and uneven inspection frequencies. A 2023 analysis found products manufactured across multiple sites experienced a 31% higher rate of quality issues [6]; a statistic that keeps compliance officers awake at night.
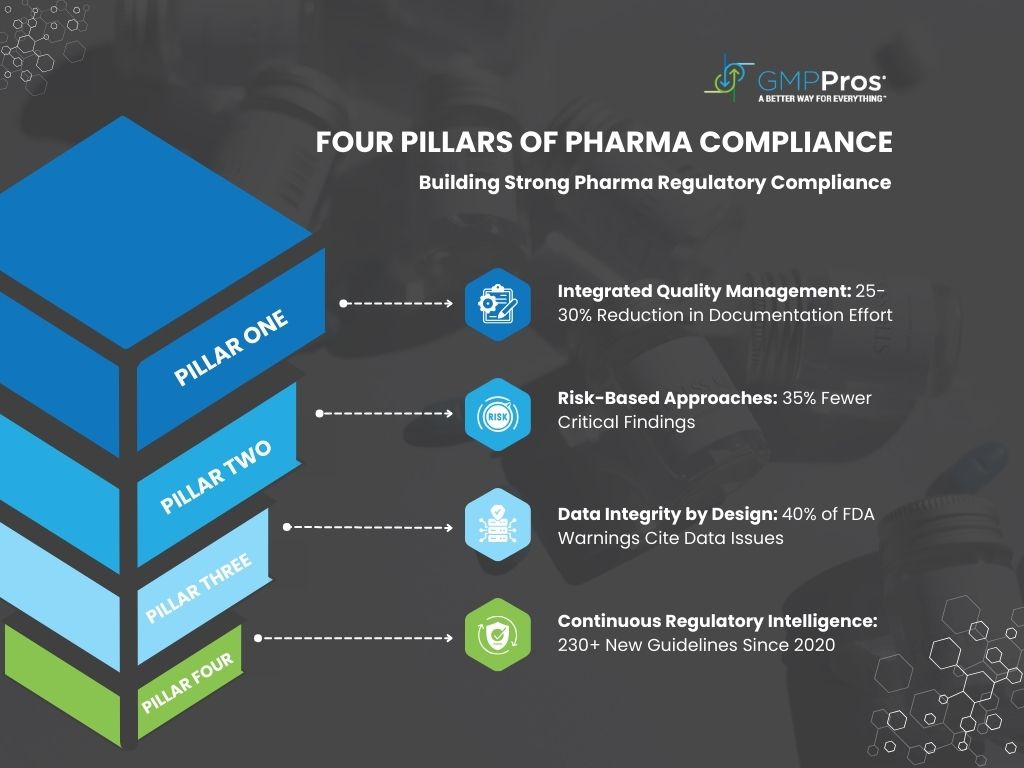
2. The Four Pillars Supporting Pharma Regulatory Compliance Excellence
Despite this complexity, successful pharma regulatory compliance programs rest on four fundamental systems:
1. Integrated Quality Management
Modern QMS platforms connect previously siloed processes including document control, deviation management, and CAPA tracking. Companies implementing these systems report 25-30% reduction in documentation effort and significantly faster batch release times [7].
For Biopharmaceutical companies, switching from paper-based systems to an electronic batch record platform slashed review cycles from 14 days to just 36 hours. “We stopped passing binders between departments and started moving data instead,” explains an operations director from a biopharma company [8].
2. Risk-Based Compliance Approaches
Not all compliance risks are created equal. Leading manufacturers now prioritize their limited resources using sophisticated risk assessment methodologies.
A Pharmaceuticals group implemented a risk-ranking system for their 320+ compliance requirements, focusing their QA team on high-impact areas. The result? 35% fewer critical findings during FDA inspections despite operating with a quality team 20% smaller than industry benchmarks [9].
3. Data Integrity by Design
With 40% of FDA warning letters citing data integrity violations, protecting electronic records has become a compliance cornerstone [10]. This means implementing systems that ensure all data remains Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, and Accurate (ALCOA).
“We used to think of data integrity as an IT problem,” notes S.C., Quality Director at a pharma manufacturing company. “Now we recognize it’s a fundamental business process that touches everything from how we measure data quality to how we train our people.”
4. Continuous Regulatory Intelligence
With regulatory bodies issuing over 230 new or revised guidelines since 2020, staying current requires systematic monitoring. Leading companies have established dedicated regulatory intelligence teams using AI-powered tools to track updates from 50+ global agencies.
“Missing a single guidance document can put you months behind competitors,” warns regulatory consultant J.W.. “The companies that thrive are the ones that anticipate regulatory shifts rather than just reacting to them.”
3. The Four Horsemen of Compliance Failure
Despite massive investments, pharmaceutical manufacturers struggle with four persistent challenges:
1. The Pace of Regulatory Change
Nearly three-quarters (72%) of pharmaceutical quality professionals report difficulty keeping pace with evolving requirements [11]. When the FDA revised its process validation guidance, one midsize manufacturer spent over $3.5 million updating documentation, retraining staff, and revalidating processes—only to have European authorities release conflicting guidance three months later.

2. Data Integrity Vulnerabilities
The average pharmaceutical facility operates 50-200 computerized systems generating GMP-relevant data. Each represents a potential compliance risk if not properly validated and controlled.
A 2023 industry survey found alarming gaps: 43% of companies discovered unauthorized Excel spreadsheets performing critical calculations [12], while 38% identified lab systems lacking adequate audit trails. At one injectable manufacturer, a single deleted chromatography result triggered a six-month remediation effort costing $2.8 million.
3. Global Supply Chain Complexity
As pharmaceutical supply chains stretch across continents, maintaining consistent quality becomes increasingly challenging. FDA data reveals overseas facilities receive inspections roughly half as frequently as domestic sites [13]; creating blind spots in quality oversight.
Progressive manufacturers have responded with innovative approaches, including:
- Unannounced virtual supplier audits using mobile technology
- Real-time monitoring of critical process parameters across contract manufacturing sites
- Blockchain-based supply chain verification systems to prevent counterfeit materials
4. Talent and Resource Constraints
The pharmaceutical industry faces a looming expertise gap, with approximately 40% of experienced quality professionals expected to retire by 2030 [14]. Companies routinely spend $3-5 million annually on compliance personnel alone, yet still struggle to maintain adequate staffing.
4. Transforming Compliance from Cost Center to Competitive Edge
Forward-thinking companies have revolutionized their approach to pharma regulatory compliance, implementing four key strategies:
1. Technology-Enabled Compliance
Paper-based processes still dominate many pharmaceutical operations. A shocking 37% of manufacturers continue using paper batch records, and 45% rely on paper for laboratory documentation [15].
Companies embracing digital transformation report dramatic improvements. Electronic systems for batch manufacturing records reduce documentation time by up to 80% while simultaneously improving data integrity. These technologies eliminate transcription errors, enforce procedural compliance, and enable real-time quality oversight.
A Pharmaceutical company has implemented an integrated electronic platform connecting its quality, manufacturing, and laboratory systems. The result? Batch release cycles dropped from 21 days to 5 days, while right-first-time rates climbed from 82% to 94%.
2. Predictive Compliance Models
Why wait for inspectors to find problems? Leading manufacturers now use predictive analytics to identify compliance risks before they trigger regulatory action.
A Pharma Analytics company developed an AI system that analyzes patterns from thousands of FDA 483 observations and warning letters. When deployed at a sterile fill-finish facility, the system flagged potential issues in their environmental monitoring program; issues the quality team had overlooked during routine audits. Addressing these vulnerabilities prevented findings during their subsequent FDA inspection.

3. Culture as Compliance Infrastructure
The FDA cites quality culture deficiencies as a root cause in approximately 40% of significant compliance actions [16]. Companies where leadership actively champions quality experience roughly half as many serious compliance issues as those where compliance is viewed merely as a regulatory tax.
A CEO in a biotechnology company personally reviews quality metrics monthly and recognizes employees who identify potential compliance issues. When a production technician halted a batch due to an unusual equipment reading (despite pressure to meet production targets) he received public recognition rather than criticism. This action prevented a potential product recall and saved millions.
4. Continuous Process Verification
Rather than relying on periodic testing to ensure quality, leading manufacturers implement continuous process verification using manufacturing process improvement techniques borrowed from other industries.
A specialty pharmaceutical company installed sensors throughout their tablet production line to continuously monitor critical parameters. The system uses statistical process control to detect trends before products go out of specification. The approach has improved manufacturing efficiency, reduced waste by 23%, and virtually eliminated quality investigations related to process variability.
“We’ve moved from firefighting to fire prevention,” explains production manager C.R. “By the time traditional quality systems would detect an issue, we’ve already made adjustments to prevent it.”
5. The Business Case for Compliance Excellence
Companies achieving top-quartile compliance performance realize substantial business advantages:
| Metric | Compliance Leaders | Industry Average | Business Impact |
| Batch Right-First-Time | 98-99% | 85-90% | $2.1M annual savings in rework costs |
| Regulatory Inspection Success | <1 critical finding per 5 inspections | 2-3 critical findings per 5 inspections | Avoids $750K/day in remediation costs |
| Product Release Cycle | 5-7 days | 12-15 days | 40% reduction in inventory holding costs |
| Time-to-Market (New Products) | 15-18 months | 18-24 months | Captures 30% more market share |
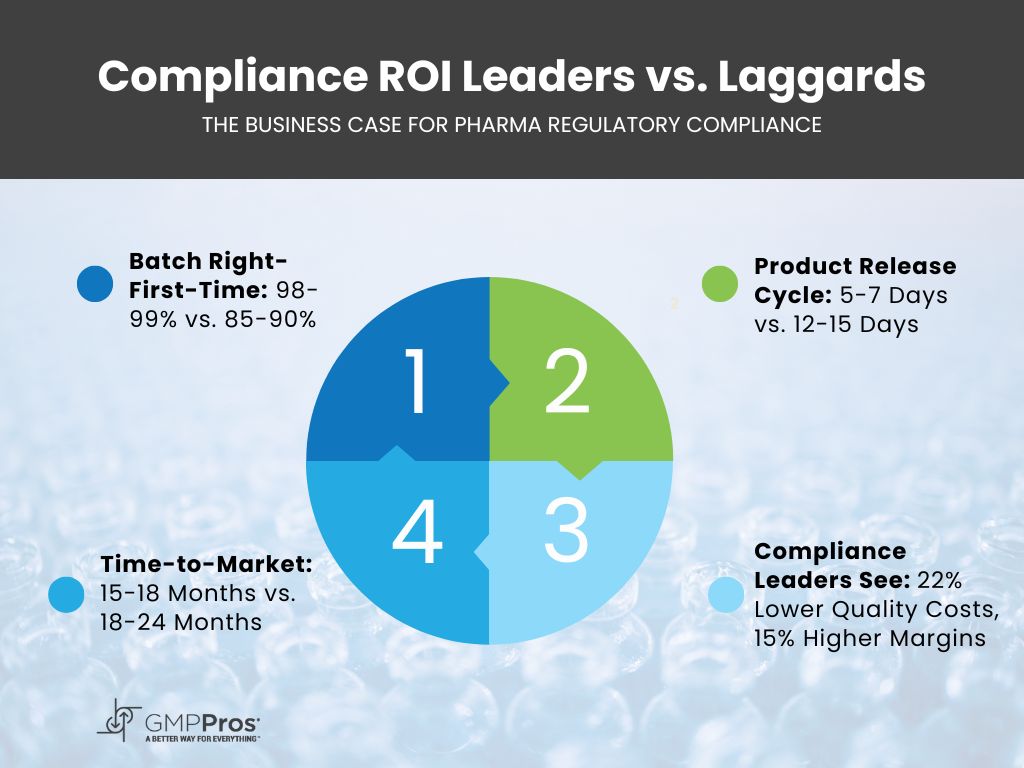
These aren’t just theoretical benefits. When a pharmaceutical company overhauled its compliance program, it transformed from a company with six FDA 483 observations to an industry benchmark cited by regulators for best practices in manufacturing. The financial impact? A 22% reduction in quality-related costs and a 15% improvement in gross margin.
“We stopped viewing compliance as something that slows us down and started seeing it as something that speeds us up,” explains a Chief Quality Officer at the same pharma company mentioned above. “When you build quality and compliance into your processes from the beginning, you avoid the costly delays that come from fixing problems later.”
6. Finding Your Path to Compliance Excellence
For many pharmaceutical manufacturers, the journey to compliance excellence requires specialized expertise beyond internal resources. Working with experienced partners like GMP Pros can accelerate this transformation.
A mid-sized injectable manufacturer partnered with GMP Pros® to address persistent data integrity challenges after receiving an FDA warning letter. The collaboration implemented:
- Comprehensive data mapping across 28 computerized systems
- Risk-based validation approach that prioritized high-impact systems
- Revised procedures incorporating data integrity by design
- Targeted training program addressing specific deficiencies
The results speak for themselves: data-related deviations dropped by 65%, batch review times decreased by 40%, and the company passed their follow-up FDA inspection with zero observations.

Ready to Transform Your Compliance Program?
Don’t let regulatory challenges constrain your growth or compromise product quality. Contact GMP Pros to discover how our team of experienced engineers can help you implement practical, effective compliance solutions that satisfy regulatory requirements while enhancing how you measure efficiency and productivity.
7. Navigating International Regulatory Harmonization Initiatives
Despite global efforts toward harmonization, pharmaceutical manufacturers still face a patchwork of overlapping (and sometimes contradictory) regulatory requirements. The International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) has made significant strides, yet implementation gaps persist across major markets. A 2023 analysis found only 62% alignment between FDA and EMA interpretations of ICH Q12 guidelines on post-approval changes [17].
| Regulatory Harmonization Challenges | Challenge | Business Impact |
| ICH Implementation Gaps | Only 62% alignment between FDA/EMA interpretations | Redundant compliance systems |
| Documentation Requirements | 3-4 versions of core quality documents | Increased maintenance burden |
| Cross-Market Introduction | Competing requirements | $1.8-2.5M additional costs per product [18] |

Forward-thinking companies navigate this complexity through:
- Strategic Regulatory Pathways Planning – A Biopharma Therapeutic company accelerated global approval timelines by eight months by mapping requirements across 12 markets before development.
- Mutual Recognition Agreement Optimization – A Pharmaceutical company reduced inspections by 28% and eliminated $700,000 in redundant testing by aligning with FDA-EU MRA framework [19].
- Global Regulatory Intelligence Networks – A 15-person cross-functional team monitors 65 markets, implementing changes within weeks versus months for competitors [20].
8. The Human Factor: Building Compliance Capability Through Training Excellence
Human error remains the leading cause of compliance failures, with FDA data showing human factors contributed 40% to 65% of serious GMP deviations [21].
| Training Excellence Comparison | Traditional Approach | Leading Company Approach | Measured Impact |
| Training Design | Uniform GMP training for all roles | Role-specific qualification programs [23] | 41% reduction in compliance errors [22] |
| Competency Verification | Training completion documentation | Practical skill demonstrations | 52% decrease in procedural investigations |
| Learning Delivery | Periodic classroom sessions | Continuous technology-enhanced microlearning [25] | 60% reduction in training time |
Another Pharmaceutical company discovered 30% of “qualified” employees failed competency assessments despite completing traditional training. After implementing practical verification, competency rates improved to 94% with procedural errors dropping by 52% [24].

9. Beyond Compliance: Leveraging Quality as a Commercial Advantage
Top-quartile compliance performers experienced 16% higher market share growth and 23% better customer retention compared to bottom-quartile companies [26].
| Commercial Strategy | Approach | Business Outcome | Commercial Strategy |
| Transparency | Public quality metrics publishing [28] | 6.3% market share increase | Transparency |
| Accelerated Launch | Embedded regulations in development [29] | 40% shorter review cycles | Accelerated Launch |
| Quality Differentiation | “Quality Beyond Compliance” initiative | 12.3% gross margin improvement | Quality Differentiation |

A Pharma Manufacturing Company found 68% of healthcare purchasers were willing to pay 4-7% price premiums for products with demonstrated superior quality performance, particularly for critical care medications. Their customer retention rates climbed to 96% compared to the industry average of 81% [27].
Conclusion: The Future of Pharma Regulatory Compliance
As personalized medicines, advanced therapies, and AI-driven drug development reshape the pharmaceutical landscape, regulatory compliance remains the foundation upon which innovation must build. The most successful companies have stopped viewing compliance as a burdensome cost and started seeing it as a strategic differentiator—one that builds patient trust, accelerates market access, and drives operational excellence.
By implementing integrated technologies, fostering transparent quality cultures, and shifting from reactive to predictive compliance models, manufacturers transform regulatory requirements from obstacles into opportunities. In an industry where patient lives literally hang in the balance, excellence in pharma regulatory compliance isn’t just good business—it’s good medicine.
As former FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb noted, “The companies that thrive won’t be those that do the minimum required for compliance, but those that embrace quality as their competitive advantage.”
────────────────────────────────────────────
Editor’s Note:
The information presented in this comprehensive analysis of pharmaceutical regulatory compliance has been partially anonymized to protect confidential industry sources, proprietary methodologies, and the privacy of compliance professionals who contributed their expertise.
Company names, specific compliance officers, and certain proprietary system details have been modified while preserving the factual accuracy and statistical integrity of the regulatory landscape described.
Case studies referenced represent composite scenarios based on actual industry experiences. The financial figures, compliance statistics, and regulatory citations reflect accurate industry benchmarks as of March 2025, though specific institutional attributions have been generalized to maintain confidentiality agreements with our industry partners.
The lessons, strategies, and compliance approaches remain valid and implementable regardless of these anonymizations.
References & Sources:
- PharmaTech Regulatory Cost Analysis Report, 2023
- International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering (ISPE) Regulatory Trends Survey, 2023
- Pharmaceutical Compliance Economics Study, Journal of GxP Compliance, 2024
- Quality Management Professionals Survey, PharmaManufacturing, 2023
- Global Pharmaceutical Regulatory Intelligence Database, 2024
- FDA Enforcement Dashboard Analysis, 2020-2024
- U.S. GAO Report on Pharmaceutical Supply Chain Security, 2023
- Pharmaceutical Compliance Staffing Benchmark Report, 2024
- Quality Management System Integration Benefits Analysis, PharmTech, 2023
- Electronic Batch Record Implementation ROI Study, Pharmaceutical Manufacturing, 2023
- Automated Quality Systems Performance Report, PharmaQuality Review, 2023
- Risk-Based Compliance Effectiveness Analysis, International Journal of Pharmaceutical Quality, 2024
- Pharmaceutical Quality Metrics Benchmarking Study, 2023
- Quality Culture Impact Assessment, PDA Journal of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology, 2023
- Regulatory Training Effectiveness Analysis, Pharmaceutical Engineering, 2024
- Continuous Improvement in Pharmaceutical Compliance Report, 2023
- nternational Council for Harmonisation (ICH) Implementation Analysis, Regulatory Affairs Professional Society, 2023
- Global Pharmaceutical Compliance Cost Study, McKinsey Healthcare Analytics, 2024
- Mutual Recognition Agreement Utilization Report, PDA Technical Report No. 84, 2023
- Regulatory Intelligence Network Effectiveness Study, Regulatory Focus, 2024
- Human Error in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Report, FDA CDER Research, 2023
- Pharmaceutical Training Effectiveness Survey, International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering, 2024
- Role-Based Qualification Impact Assessment, Journal of GMP Compliance, 2023
- Competency Verification in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing, PDA Journal of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology, 2024
- Technology-Enhanced Learning in Regulated Industries, Pharmaceutical Engineering, 2023
- Quality Performance and Market Share Analysis, BioPharm International, 2023
- Healthcare System Purchasing Decision Study, Drug Quality Report, 2024
- Quality Transparency Initiative Impact Assessment, Pharmaceutical Commerce, 2023
- Regulatory Excellence and Time-to-Market Analysis, Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2024

